Unit 2 Chemistry
The Big Idea: The kinetic molecular theory and the theory of the atom explain the behaviour of matter.
Before you begin...
- Complete all of the sections below including watching videos, answering questions and doing activities.
- ALL questions must be answered in COMPLETE SENTENCES and handed into your teacher.
2.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory
In this section we'll think about the following question:
How does kinetic energy help explain the states of matter?
How does kinetic energy help explain the states of matter?
|
Download the section questions, hand them in to your teacher when you're done.
|
| ||||||
|
|
States of Matter VideoTextbook Work:
|
|
|
Matter Video |
|
|
Potential and Kinetic Energy VideoTextbook Work:
|
|
|
The Kinetic Molecular Theory Video |
Section 2.1 Final Activities
|
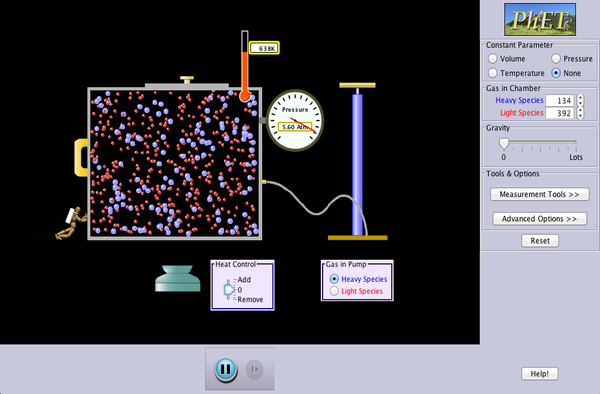
Gas Chamber Activity
Follow these instructions below and answer the questions on a piece of paper then hand it in to your teacher:
|
|
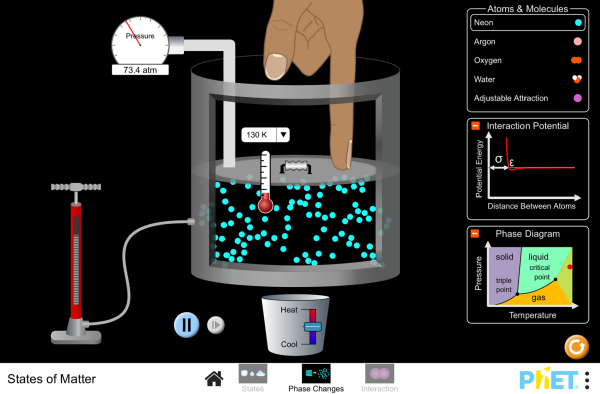
States of Matter Activity
Follow these instructions below and answer the questions on a piece of paper then hand it in to your teacher:
|
~ ~ ~ Hand in section 2.1 to your teacher ~ ~ ~
2.2 Atomic Theory
In this section we'll think about the following question:
If atoms are invisible to the naked eye, how do we know they exist?
If atoms are invisible to the naked eye, how do we know they exist?
|
Download the section questions, hand them in to your teacher when you're done.
|
| ||||||
Dalton's Atomic Theory Video
How do we know that things are really made of atoms?

Go to the BBC article by Chris Baraniuk. As you read answer the following questions:
- Can you see an atom under a microscope?
- What makes an object visible under a microscope?
- Do atoms deflect light?
- What Greek word does the word 'atom' derive from and what does it mean?
- What three parts are atoms made up of?
- How does the article describe an atom? (hint: sun)
- If subatomic particles (ex. electrons) are so small, how do we know they're there?
- JJ Tomson discovered the electron using an experiment called the Cathode Ray Tube. Watch the video below to see how this experiment was conducted. This experiment is extremely clever, and a little tricky to understand, so don't stress if this sounds like gibberish to you.
- Are atoms solid little pieces of matter?
- Ernest Rutherford contributed to the discovery of the proton. Watch the video below to see how this experiment was conducted.
- You may stop reading the article at this point.
|
|
JJ Tomson's Cathod Ray Tube |
|
|
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment |
~ ~ ~ Hand in section 2.2 to your teacher ~ ~ ~
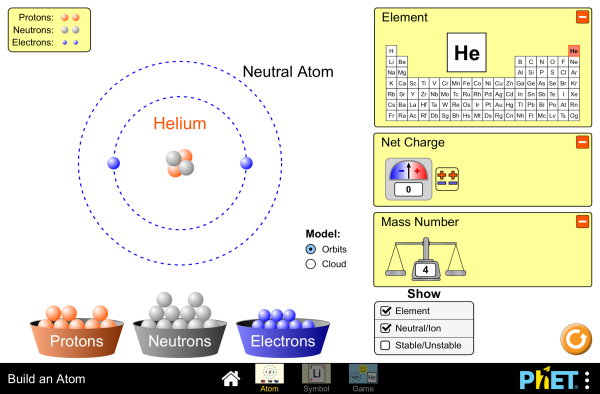
2.3 Atoms
In this section we'll think about the following question:
What makes up an atom?
|
Download the section questions, hand them in to your teacher when you're done.
|
| ||||||
|
|
What is an atom? |
|
|
How small is an atom? Spoiler: Very Small |
|
|
What is the Periodic Table of Elements?Download the Periodic Table, it will be helpful to use it to follow along with the video.
|
~ ~ ~ Hand in section 2.3 to your teacher ~ ~ ~
2.4 Quarks and Leptons
In this section we'll think about the following question:
What holds the subatomic particles together?
|
Download the section questions, hand them in to your teacher when you're done.
|
| ||||||
|
|
Strong Interaction |
|
|
What are Quarks |
The Particle AdventureDownload and complete the following activity, courtesy of QuarkNet.
| |||||||